Search Results
Results for: 'Chlorine ion'
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 6873
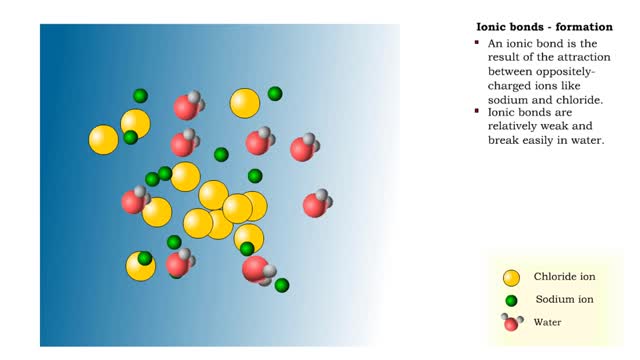
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
By: HWC, Views: 5458
The slight positive charge of a hydrogen atom in a water molecule can attract an atom with a slight negative charge, such as the nitrogen in a molecule of ammonia. This forms a hydrogen bond between the two atoms. Hydrogen bonds join the two strands of a DNA molecule. Although hydrogen bo...
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 3982
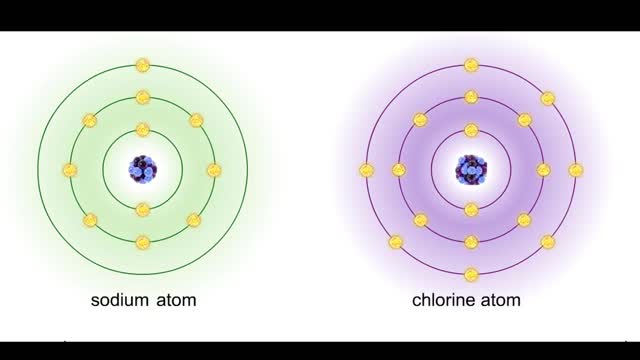
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
Advertisement